How to cure gum disease? Gum disease treatment in dental clinic
In our daily routine, while we brush our teeth, we probably take a rapid glance at our teeth at least for a few seconds in the mirror to see how bright and healthy they look! But do we also observe and care about our gums? Unfortunately, most of us think that dental health is only about our teeth. But not surprisingly, the gums also provide valuable information about the condition of our teeth and dental health.

Gum health and dental health are closely associated. To put it more clearly, gum health is an indispensable part of dental health. For this reason, we need to observe the condition of our gums very closely while brushing our teeth at least twice a day. When you look at your gums in the mirror and notice that they are swollen, you should know that you may have some type of gum disease.

Gum disease can be seen in all age groups, progresses slowly, and may not be noticed immediately. If the gums are not properly taken care of, ongoing problems of the gum may eventually spread to the surrounding bones and even result in tooth loss if left untreated. You may wonder whether the symptoms of gum disease are limited to swollen and reddened areas on the gums or not. Needless to say, the symptoms of gum disease are not limited to these indicators. You may learn more about the most common symptoms of gum disease in the following section.
What are the most common symptoms of gum disease?
The most common symptoms of gum disease can be summarized as follows:
- Recession of the gums (The gums recede, causing the teeth to appear longer)
- Enlargement of the gums
- Discoloration of the gums (bright red, dark red, blue or purple colour)
- Swelling of the gums
- Teeth wobbling or displacement
- Formation of new gaps between the teeth
- Blood while brushing teeth
- Cavity between tooth and gum
- Painful chewing
- Mouth odor
- Bad taste in the mouth
- Sensitivity of the gums during eating and drinking
If you have any of the symptoms mentioned above, you ought to consult a dental clinic immediately. Your dentist will identify the underlying problem and will save you from this problem by determining the appropriate treatment method. Remember that if you are late in the detection and treatment of your gum disease, this may cause the loss of your teeth and even further complications in your overall health condition.
What are the causes of gum disease?
In order to avoid gum disease, we first need to know what causes gum disease. If we eliminate the following causes, we will reduce our risk of developing gum disease. The common causes of gum disease are listed below.
Plaque:
Dental plaque is the main cause of gum disease. Plaque is a film of bacteria that builds up on teeth and at the gum line. If left untreated, plaque eventually turns into tartar, which can lead to gum infection.
Insufficient oral hygiene
The main cause of plaque formation in the teeth is insufficient oral hygiene. If you do not brush your teeth regularly and do not use dental floss, plaque formation on your teeth is inevitable. Plaque formation will eventually cause inflammation and infection of the gums.
Smoking:
Tobacco damages gum tissues and delays the healing of infection in your gums.
Malnutrition:
If you do not take foods containing the vitamins necessary for your body and teeth, your immune system weakens and your gums are adversely affected. It is advisable to consume meals rich in vitamins C and K.
Genetic factors
If there are people in your family who are prone to gum disease, you may also carry the risk of having gum disease.
Diseases including Diabetes, Leukemia, Cardiovascular Diseases, and AIDS:
Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes negatively impact multiple organs in the body and delay wound healing. One of these is our gingiva. Elevated blood glucose levels can impede the healing of periodontal infections. Diabetes can also lead to other illnesses, including periodontal disorders and dental caries. Diseases such as leukemia, cardiovascular diseases, and AIDS can also trigger gum disease as they weaken the gums.
Stress:
Like malnutrition, stress weakens the immune system and can weaken your body's fight against infections. This will make your gums more vulnerable to any possible infection.
Hormonal Changes:
Hormonal changes such as menstruation, pregnancy, and menopause make the gums more sensitive and increase the risk of inflammation.
Regularly Used Drugs:
Regularly taken blood pressure and antidepressant drugs may induce a dry mouth. These medications will elevate the risk of periodontal disease by diminishing the efficacy of saliva.
What are the types of gum disease?
Gum diseases can be categorized based on the anatomical location (peripheral bones, teeth, gums, jawbone, intraoral problems, etc.) and the severity of the disease.
Abscess:
An abscess is a swelling in the gums, periodontal fibers, and jawbone. If there is dental decay, an abscess may develop. It can also happen if a tooth is chipped, cracked, or otherwise damaged. Bacteria can infect the pulp, the interior of the tooth, through holes in the tooth enamel. From the tooth's root to the jawbone, the infection may continue to grow and spread.
Gingivitis:
Infections from plaque and tartar impact the gums, resulting in halitosis. As typical implications of gingivitis, we note hemorrhaging, erythema, and edema of the gingiva. Neglected gingivitis can lead to the infection extending to the periodontal fibers that sustain the gums or perhaps to the jawbone.
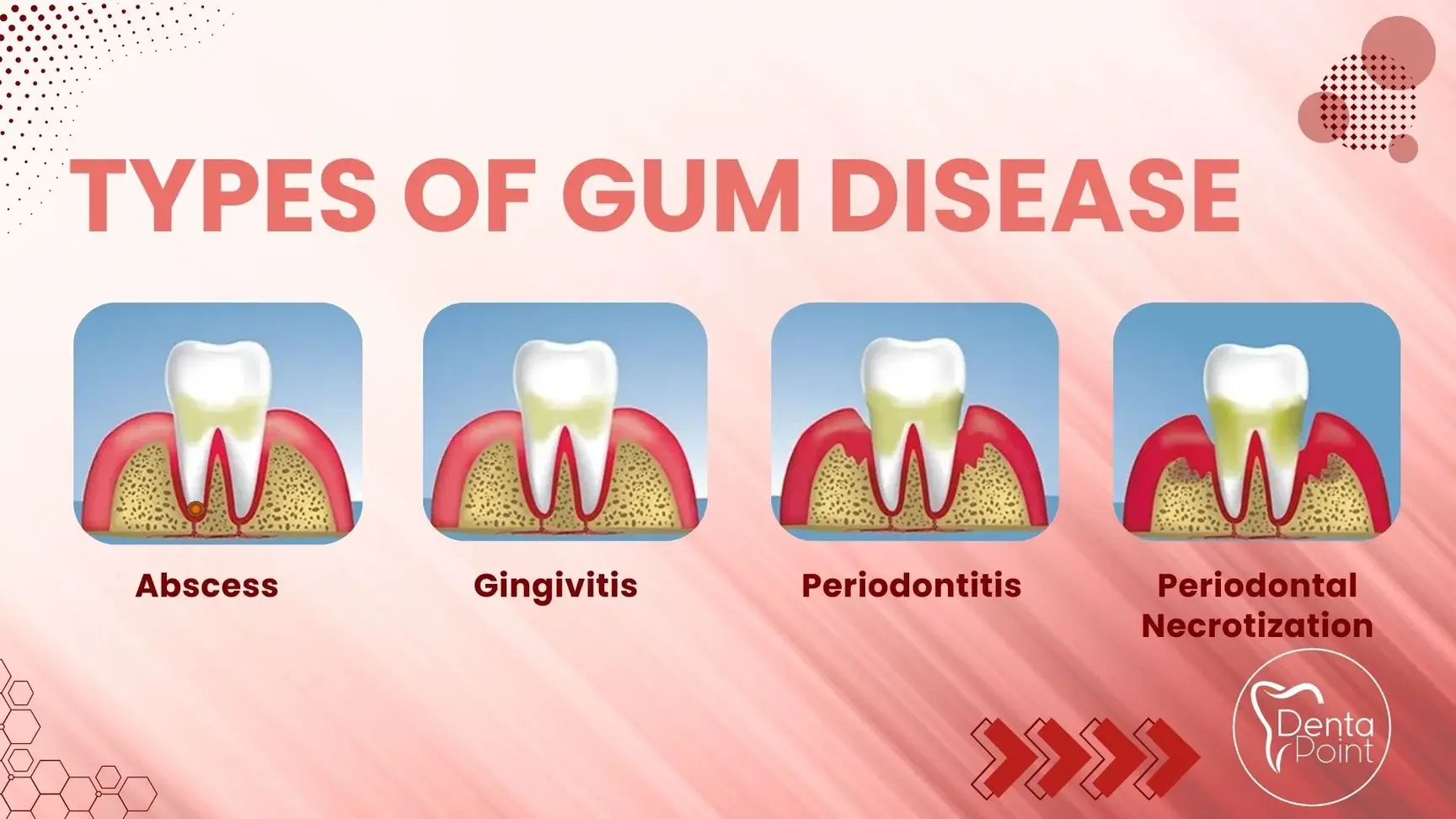
Periodontitis:
This is a condition in which gingivitis is left untreated and the infection progresses to the periodontal fibers and the jawbone. Bacteria begin to accumulate in the space between the teeth and gums called the periodontal pocket and the disease progresses. If this condition remains untreated, the tooth roots deteriorate, causing the teeth to wobble and potentially necessitating the pull-out of the tooth.
Periodontal Necrotization:
Immune system issues and weakening of the gum tissue cause this rare disease. It may show symptoms such as pain in the gums, swelling, and discoloration of the gum tissue. This may induce overall inflammation of the mouth.
How to diagnose gum disease?
If you have any of the symptoms of gum disease described above, you should go to the dentist immediately. After you reach a dental clinic for gum disease, the procedure will generally follow as described below.
Making a diagnosis:
Your dentist may follow the steps describe below to determine the type of your gum disease and its severity:
- Check through your medical history to detect any possible causes of your symptoms. Smoking and using some medications that induce dry mouth may be detected as two examples.
- Check for easy bleeding of your gums and examine for plaque and tartar accumulation in your mouth.
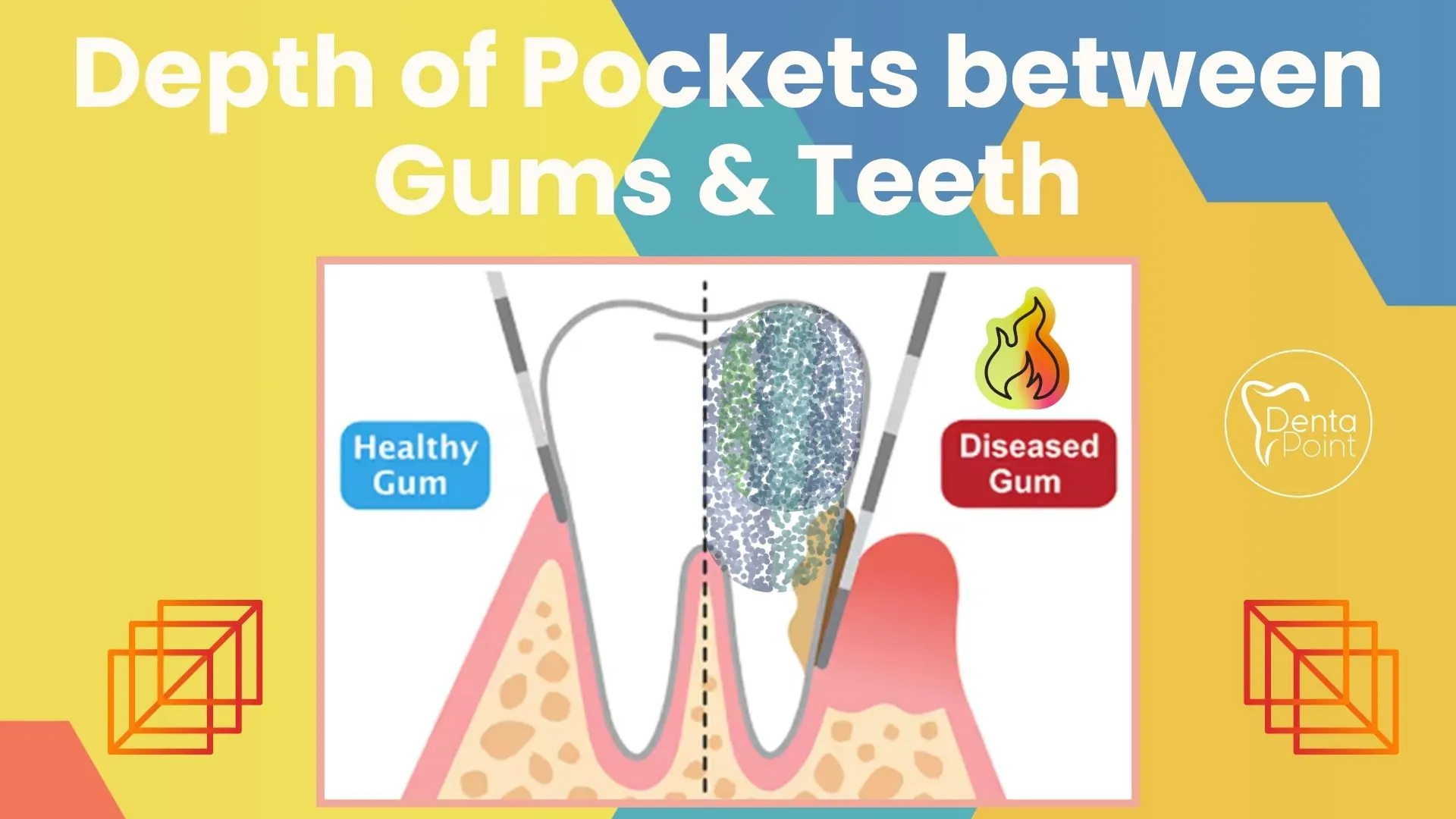
- Put a little ruler, known as a dental probe, between your teeth and gum line to determine the depth of the pockets between your gums and teeth. Your upper and lower gums' pockets are measured in multiple locations. The pocket depth in a healthy mouth is typically one to three millimeters (mm). One of the gum diseases, periodontitis, for example, may be indicated by pockets that are more than 4 mm deep. As a general practice, routine treatment cannot effectively clear pockets deeper than 5 mm.
- If your dentist notices bigger pockets, dental X-rays should be necessary to look for bone loss.
How to cure gum disease?
After diagnosing gum disease, medical intervention to cure gum disease will be planned by the expert dentists in your dental clinic. The treatment method may differentiate whether it includes surgical operation or not.
Treatments without surgery:
Less intrusive techniques may be applied for gum disease if the disease has not worsened. These techniques may be outlined as follows:
- Dental Scaling: Getting rid of tartar and bacteria from the surfaces of your teeth and under your gum line by using a laser, an ultrasonic device, or other necessary tools.
- Root Planing: The root surfaces are smoothed by root planing. This lessens the chance of germs and tartar accumulation. Additionally, it facilitates the reattachment of your gums to your teeth.
- Drug Therapy: Oral or topical antibiotics can contribute to the management of bacterial infections. Antibiotic mouthwashes and applying gel with an antibiotic to gum pockets are examples of topical antibiotics. Oral medicines are occasionally required to eradicate infection-causing microorganisms.
Treatments with surgical operation:
- Pocket Reduction Surgery: Periodontist skilfully folds back the tissue by making incisions in your gums. This enables the surgical operation for more effective scaling and root planing.
- Soft Tissue Graft, Guided Tissue Regeneration (GTR): Your gum line lowers and some of your tooth roots become visible when you lose gum tissue. Some of the injured tissue might require reinforcement. Usually, to accomplish this, a tiny piece of tissue from the roof of your mouth is removed, or tissue from another donor source is attached to the damaged area.This can prevent further gum loss, conceal exposed roots, and make your teeth seem better.
- Bone Graft, Guided Bone Regeneration (GBR): This method is practiced when the bone around your tooth root is destroyed. Small pieces of your bone may be used for the transplant, or the bone may be donated or produced of synthetic material. By keeping your tooth in place, the bone graft helps stop tooth loss. Additionally, it provides a surface on which natural bone can rebuild.
Frequently asked questions and humble answers from the perspective of dental experts
How to cure gum disease without a dentist? Is it possible?
If you are having a problem with your gums, getting rid of gum disease without a dentist will most likely not be possible. For example, without treatment in a dental clinic, a tooth abscess won't disappear. The discomfort may significantly subside if the abscess ruptures, leading you to believe that the issue has been resolved; nonetheless, dental care is still necessary. Your jaw and even other parts of your head and neck could become infected if the abscess doesn't drain.
There are some home remedies for gum health. These remedies are quite useful to keep the healthy status of your gums provided that your gums are not infected. If there is an infection in your gums, then you should consult a dental clinic to get rid of bacteria from your gums and prevent further spread of infection to other parts of the body such as parts of your head and neck. After the necessary treatment is applied, your dentist may provide you with necessary suggestions to keep your gums healthy including the best mouthwash for gum disease or the best toothpaste for gum disease etc.
Can gum disease heal on its own?
Gums that are swollen, red, and bleeding are the first symptoms. The severity of gum disease increases if treatment is not received. Your tooth may become loose and could fall out if bone loss persists. For the serious cases of gum disease, gum bleeding is frequently accompanied by pus and infection around the gum line, which can result in persistent bad breath.
What happens if I have gum disease for too long?
It is an undeniable medical fact that any infection might spread in case it is not treated. Likewise, the infection of gums has the potential to spread to other regions of your mouth and body, raising your chance of developing diabetes, heart disease, stroke etc. If you have gum disease for too long without any medical treatment, it may eventually negatively impact your oral and general health.
Is gum disease contagious?
In general terms yes, it is contagious. Saliva is one way that the gum disease bacteria can spread. The other person may thus be at a higher risk of developing gum disease as a result of saliva-to-saliva contact if you have gum disease.
Is gum disease hereditary?
According to researches, heredity may play a role in periodontal disease, therefore your genetic composition may actually increase your risk of developing gum disease.
Final Remarks
If you have a gum disease problem, you should definitely consult a dental clinic at the earliest opportunity and follow the recommendations and possible treatment plan that your dentist will suggest. Any delay in consulting your dental clinic and trying to find solutions on your own at home may cause your oral and dental health to deteriorate even more.
As is the case with almost all health problems, early diagnosis and treatment of gum disease will save you from possible bad consequences. Failure to receive professional treatment for gum diseases starts with the loss of the tooth and involves risks that can lead to even heart attacks.
Gum disease can be treated in the early stages. The expert team at DentaPoint Dental Clinics will apply the necessary treatment methods you need for gum disease and will help you protect your oral health. You may also take a look at the NHS Page for gum disease.


